February 2020 took the healthcare sector by surprise, compelling clinicians to rethink their posture towards emerging technologies in medicine. In today’s world, innovations are undoubtedly part and parcel of the human experience but with sociological values constantly changing, current models of digital age technology struggle to keep up with them, leaving many people concerned about their relevance, usage and objective.
Thus, more than ever before, people are relying on the health sector as the last bastion for relevant and helpful answers to their day-to-day anxieties.
This, therefore, begs the question of how we can unimpeachably harness eHealth tools to ensure consumer assurance and confidence. This is the general focus of this article, with its specific points being:
- Contemporary and trending healthcare innovations
- The crucial importance of delivering high-quality eHealth apps
- The case for effective deployment.
Current medicine tech trend
The days of sweeping clinical services are gone and personalized treatment is in because each individual responds differently to the same ailment. This personalized approach relies on access to big data, and the internet of things (in medicine) to accurately decode patient genetic information.
The onset of the pandemic forced us to leverage unconventional medical solutions to survive its unprecedented onslaught. Facing lockdown, telemedicine reigned supreme as people remotely interacted to make complaints and receive medical attention. Virtual consultations have since increased fifteen times over. It is largely dependent on telecom technology and smartphone usage. A Statista survey revealed that 70% of respondents prefer using their mobile devices to notify their clinic about their health conditions, risk zones and to collect data of symptoms.
Artificial Intelligence is also in big time. Although AI has been a prevalent technology for a while, its use in medicine is now a phenomenally growing trend. The World Quality Report 2019-2020 reveals a more-than-average gross investment of the healthcare sector in artificial intelligence with more medical organizations in line to introduce it.
Today, AI technology is employed in diagnoses, prescription, treatment and a lot more. Frost & Sullivan estimates an over 40% growth of AI use in the healthcare sector annually. Thus, by year end 2021, medicine-related AI should boast of about $6.6 billion market share.
Medical institutions are increasingly deploying electronic systems with high data storage capacity for patients’ information. Big Data technology helps organize this information into one unit that can be accessed by any healthcare center.
Patients’ means of treatment can be predicted by machine learning algorithms. With the aid of these emerging technologies, people have greater opportunities to choose satisfactory medical care.
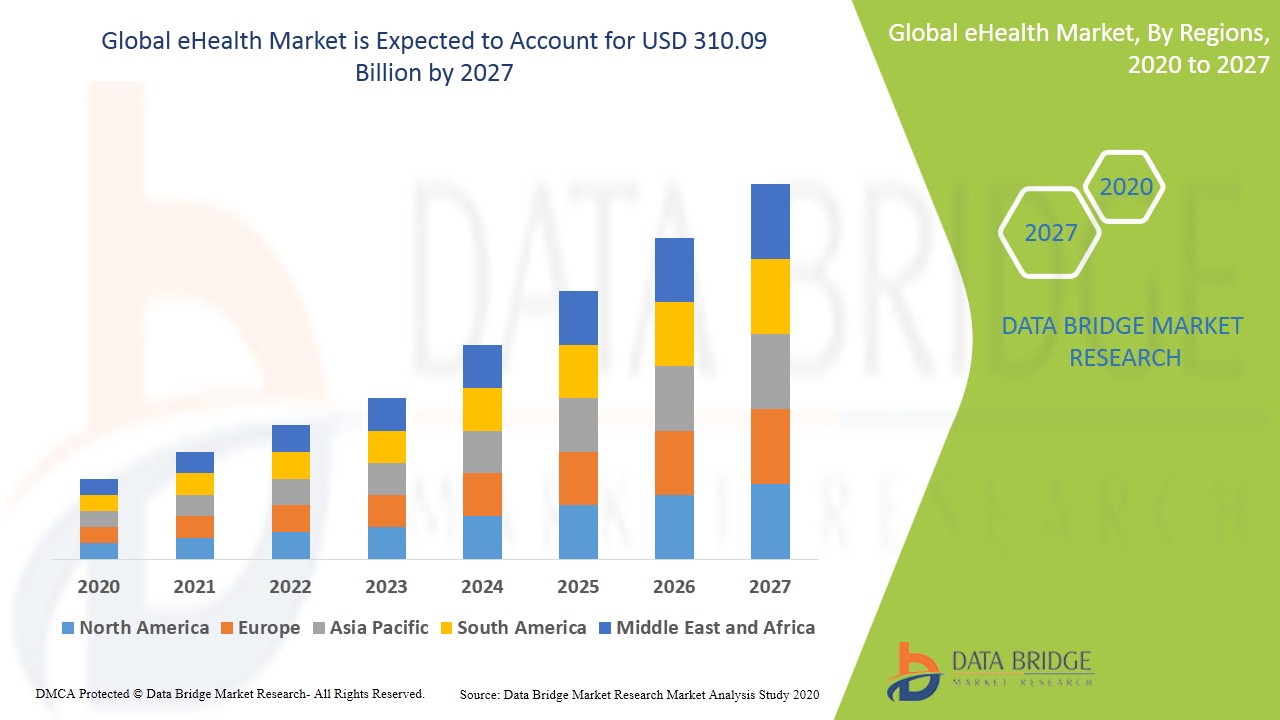
According to DataBridgeMarketResearch, the global eHealth market will exceed $310 billion in volume by 2027.
The significance of Quality Assurance in E-HEALTH
In the digitalized world of today, it is no surprise that the development and implementation of IT solutions and cutting edge new technologies is on the rise in healthcare institutions. However, as important as acquiring the technology is, its correct and beneficial deployment is crucial. And this can only be achieved through thorough testing of the software under real conditions before going live.
It cannot be overemphasized that any error in a medical solution is a matter of life and death. For instance, the occasional mistaken switching of health test results may at best cause wrong treatment or, at worst, no treatment at all; both of which could have grave consequences. Just as bad, is the faulty configuration of clinical equipment which ruin parameters for the given health condition and could lead to fatalities.
By engaging the use of Big Data technology for electronic document management, the security of information in medical organizations is much improved. Naturally, eHealth solutions are not immune to cyber-attacksof any kind. Occasionally, we hear disheartening reports of data theft or illegitimate sharing of customer information with third parties (ad agencies, credit agencies, other private organizations), and this can be a big problem. Every data system used in the healthcare industry should be developed in strict compliance with the security and confidentiality requirements defined by GDPR in the EU, and HIPAA and COPPA in the USA. With these measures in place, users are allowed to demand the erasure of their information, or an explanation of the reason for their continued storage.
Thorough pre-deployment testing will prevent all possible issues and shortcomings of IT solutions, forestalling data thefts or leaks, customer disillusionment and the collapse of an organization’s reputation.
E-Health QA: Effective Testing
According to the World Quality Report, Agile software development has been the dominant development approach in the healthcare sector for the last couple of years. However, organizations still encounter challenges in its use, particular regarding the provision of an adequate test automation level.
Given the responsibility for human well-being and the possibility of development errors, these healthcare applications must be thoroughly tested.
Functional testing
The gravity of functional checks can be buttressed by this story about alqa’s success in providing QA services for one of the leading names in Medical equipment production. Their task was to test the leading brand’s system for the collection, storage and processing of session data from blood transfusion instruments.
Following an assessment of the safety class by the IEC 62304 standard, the system was assigned the Class C, signaling the possibility of death or serious injury. Given such severe assessment, professional QA engineers were recruited after having to pass the mandatory introductory course. These engineers worked on the functionality of the software getting it compliant with IEC 62304 standards.
Functional testing by this alqa specialists involved smoke tests to ensure there were no serious issues that could hamper further activities. Defect validation and regression testing helped to make sure that units developed previously were unaffected by any changes.
Performance testing
A system involving a huge amount of data typically handles multiple simultaneous operations regularly, which could affect system stability. Thus, a1qa experts recommend that heavy-load response and simultaneous-sessions checks be carried out on the software before it goes into production. These experts apply user behavior to foster a seamless operation of the medical system. They simulate the actions of real users to assess the reaction of the system given multiple operations and heavy load.
Big data testing
The a1qa firm has had the experience of ensuring data accuracy for a corporation that services pharmaceutical companies. The central challenges were streamlining the complicated maze of customer databases and the volume of system work load. Nevertheless, the experts were able to successfully fine-tune big data testing leading to improved product quality.
Because integrity and completeness are the building blocks of a secure patient data transferring process that can be adopted by medical institutions wholesale, performance testing is non-negotiable.
Test automation
Healthcare IT solutions require absolutely accurate testing hence automated testing. Although test automation minimizes the possibility of human errors, it is not a magic wand. According to the World Quality Report, developers of eHealth solutions struggle to implement test automation owing to unprofessional tools, skills and the limitations of the testing environments.
Institutions should jettison the manual process and introduce a lean automation strategy which means that each given case is only worthy of automation if it is to be in place for some time, and will be frequently checked.
Summary
Following the pandemic, medical care entered a new era involving personalized treatments, information technology, and process optimization. One thing remained constant: The grave consequences of human errors. To minimize this, eHealth products must undergo effective and rigorous tests to complement and not undermine the doctors’ efforts. After all, innovation is to help them save lives, not lose them.